
Preliminaries : This Practical Work uses version 3.0 of the scientific
software Scilab , developed by INRIA
and ENPC. All the installation files
can be downloaded freely from the web page
http://www.scilab.org.
The PW needs two Scilab command files
simu1.sce
and
simu2.sce, that one should store in his
working directory.

The aim of the PW is to study different harvesting policies of a stock of a renewable resource. More precisely, we consider a population
dynamics, whose stock follows a natural logistic growth law
and is harvested (by catches, picking, ...). The dynamical evolution of the stock can be written with the help of a ordinary differential equation :
In order to simulate the solutions of the system under Scilab , let us start by defining the dynamics and the control, with the help of two functions
![]() and
and ![]() :
:
1. For the logistic law :
2. For the control, begin by a simple law : a constant policy, as long as the stock is non empty :
deff('[u]=har(t,x)','if x>0 then u=H; else u=0; end');
and choose a value for the constant ![]() , say
, say
H=0.24;
For launching the simulations, enter the following instruction
exec("simu1.sce");
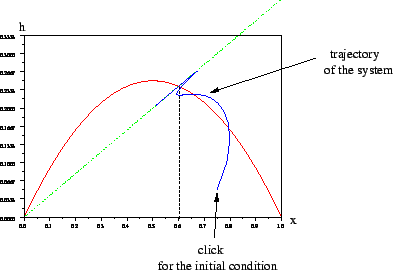
Then, a window appears :
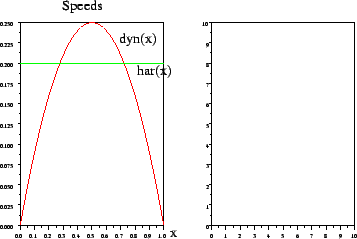
In the left, the graphs of the functions ![]() and
and ![]() are plotted.
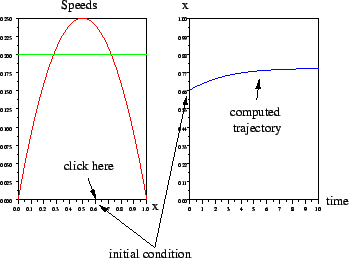
Clicking on the LEFT figure launches on the RIGHT figure
the simulation of the trajectory of the dynamical system
are plotted.
Clicking on the LEFT figure launches on the RIGHT figure
the simulation of the trajectory of the dynamical system
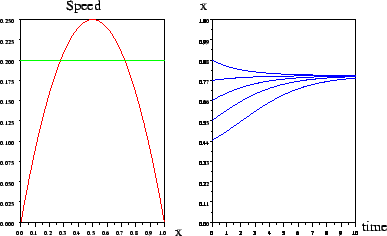
Further clicks will make different trajectories of the system superposing :
Question 1 : Study the stability of the two non-null equilibria. What is
the value ![]() of the stock at the stable equilibrium ?
of the stock at the stable equilibrium ?
Question 2 : Redefine the control law ![]() such that there exists only
on non null equilibrium
such that there exists only
on non null equilibrium ![]() , and such that from any non null initial condition, the trajectory converges asymptotically towards
, and such that from any non null initial condition, the trajectory converges asymptotically towards ![]() . Denote
. Denote
x_e=0.6;
Question 3 : We consider here that the intrinsic growth rate ![]() fluctuates with time in the following manner :
fluctuates with time in the following manner :
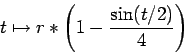
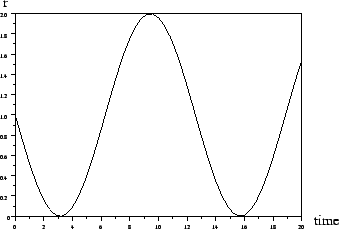
We call harvesting effort the measure of the means available for the
captures (fishermen numbers, size and number of nets, ...).
We shall assume that the harvesting speed ![]() is proportional to the stock
is proportional to the stock
![]() and the effort
and the effort ![]() at any time t :
at any time t :
We consider now an exploitation controlled by the variations of the
harvesting effort :
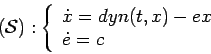
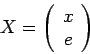
![\begin{displaymath}
({\cal C}) :
c(t) \in \left\vert\begin{array}{ll}
\left[-\ba...
...ft[-\bar c,0\right] & \mbox{ if } e=e_{max}
\end{array}\right.
\end{displaymath}](img30.png)
Question 4 : Prove that for such control laws, the domain
![\begin{displaymath}
{\cal D} = \left\{ \left(\begin{array}{c}x e
\end{array}\right) \vert x \in [0,K], \; e \in [0,e_{max}] \right\}
\end{displaymath}](img31.png)
We study now possible control laws which fulfill the constraints ![]() and stabilize the system
and stabilize the system ![]() about
about ![]() .
Three laws are considered :
.
Three laws are considered :
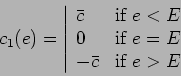
![\begin{displaymath}
\mbox{sat}_{[m,M]} : \xi \to \left\vert\begin{array}{ll}
M &...
... \xi \in [m,M]\\
m & \mbox{if } \xi \leq m
\end{array}\right.
\end{displaymath}](img43.png)
Define
H=0.24;x_e=0.6;E=H/x_e;cbar=0.1;
For the simulations, consider that ![]() is again constant, which amounts to
define the dynamics as follows :
is again constant, which amounts to
define the dynamics as follows :
deff('[y]=dyn(t,x)','y=r*x*(1-x/K)');
The control law is defined in Scilab with the help of the function ![]() .
For instance, for the ``bang-bang'' law :
.
For instance, for the ``bang-bang'' law :
epsilon=1e-3;
deff('[edot]=com(t,X)','e=X(2);..
if abs(e-E)< epsilon then edot=0;..
else edot=cbar*sign(E-e); end');
Simulations are launched entering the instruction
exec("simu2.sce");
A window then appears :
Question 5 :
Simulate the control law ![]() . What happens if one takes
epsilon=0 ?
. What happens if one takes
epsilon=0 ?
Question 6 :
Write in Scilab the control law ![]() , and simulate the trajectories
taking different values of the gain
, and simulate the trajectories
taking different values of the gain ![]() between
between ![]() and
and ![]() .
Explain the qualitative behaviors ?
.
Explain the qualitative behaviors ?
Question 7 :
Write in Scilab the control law ![]() , and simulate the trajectories
taking different values of the gains
, and simulate the trajectories
taking different values of the gains ![]() and
and ![]() . Determine
analytically the pairs
. Determine
analytically the pairs ![]() insuring a local asymptotic
stability of the closed loop system.
insuring a local asymptotic
stability of the closed loop system.
With the option :
linearise='on';
activated, entering the instruction exec("simu2.sce"); computes
and draws (in dashed lines) in addition the trajectory of the system ![]() linearized about
linearized about ![]() , in the plane
, in the plane ![]() :
:
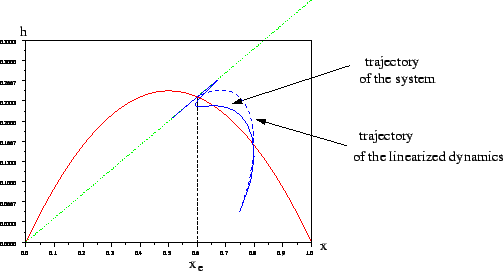
Question 8 : Launch gain the simulations of the different control laws,
together with the drawing of the trajectories of the linearized dynamics
What can be concluded ?
Practical Work sheet prepared by Pierre Cartigny and Alain Rapaport.